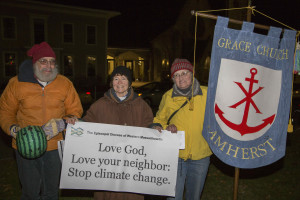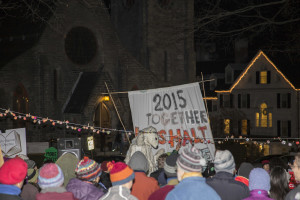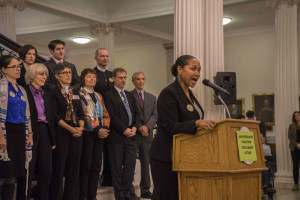On December 12, 2015, the same day that nearly 200 nations adopted a historic pledge to lower their carbon emissions, more than two thousand people from across New England marched and rallied in Boston in the biggest climate justice demonstration that the city has ever seen. A wide range of groups were represented, including, among others, the Council on American-Islamic Relations, Maine’s Penobscot Tribe, National Nurses United, New Bedford Worker Center, 350 Massachusetts, Mothers Out Front, and Climate Action NOW. I spoke on behalf of the Episcopal Diocese of Western Massachusetts and the newly formed MA Interfaith Coalition for Climate Action. The crowd cheered when I mentioned that faith groups are involved in the climate justice movement.
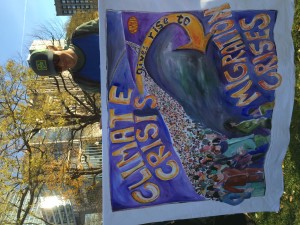
Whatever mood you were in, there was a banner or a sign to express it: sarcastic (Billionaires for Fossil Fuels) and mournful (Where have all the icebergs gone?), winsome (Save the Earth: It’s the only planet with music) and worried (It’s December and I’m wearing a T-shirt), urgent (Climate delay = global collapse) and resolute (System change, not climate change).
We started with a rally at the Parkman Bandstand on the Boston Common, but we didn’t just stand around, listening to speeches: accompanied by a marching band, we also chanted and sang our way through the streets of Boston. After marching for a mile and half, we held a closing rally in front of the State House. (For Michael Horan’s brief video montage of the march, visit here.)
The U.N. climate deal is an historic first: countries have pledged to rein in their carbon emissions and have expressed an aspiration to limit global warming to no more than 2 degrees and maybe even 1.5 degrees Celsius above average temperatures at the start of the Industrial Revolution. Yet the pledges are voluntary, and, even if carried out, insufficient to avert catastrophe. As Bill McKibben quickly observed in the New York Times, “we need to build the movement even bigger in the coming years, so that the Paris agreement turns into a floor and not a ceiling for action.” In a separate article for Grist, McKibben commented that although the international climate pact gives us reasons to be cynical, we still have reasons to hope: we must build a movement to hold countries to their promises (“What, you want to build a pipeline? I thought you were going to go for 1.5 degrees. You want to frack? Are you fracking kidding me? You said you were going for 2 degrees at the absolute worst.”)
Meeting the 1.5 or even 2-degree target will not be easy, McKibben writes in yet another article (boy, he is fast), “given that we’re currently on track for between 4C and 5C. Our only hope is to decisively pick up the pace. In fact, pace is now the key word for climate. Not where we’re going, but how fast we’re going there. Pace – velocity, speed, rate, momentum, tempo. That’s what matters from here on in.”
One of my favorite placards at the Boston rally proclaimed:
3500-2500 B.C. Bronze Age
1800-2015 A.D. Fossil Fuel Age
Do we believe that 2015 marks the end of the Fossil Fuel Age? That’s what the U.N. climate deal in Paris has promised. But that promise won’t come true all by itself. If we want it to come true and are serious about wanting to preserve a habitable world, we’ll have to work for it – to organize, lobby, vote, pray, invent, create, protest, and push – to do it together and do it fast.
We’ll do it because we’re committed to the message proclaimed by another sign:
Love will win.
Here is the speech I gave at the rally in front of the State House:

Friends, I am thrilled to be with you today as we express our shared commitment to a world that works for everyone.
We walked a fair distance to get here, and I invite you to take a moment to feel the sensation of your feet making contact with the ground. Feel the support of the earth under your feet, and let’s notice for a moment that whoever we are – wherever we come from, whatever we do for a living, whatever the color of our skin, whatever our religion or political party, we all stand on one earth. We have just one home, this home, this beloved planet on which all life depends.
I invite you to take a couple of deep breaths and to notice that wherever you’re standing, whether you’re up front or in the middle or the edge of the crowd, we’re all breathing the same air. We’re all immersed in the one atmosphere that we share, taking into our lungs the one flowing mix of gases that encircles the globe and sustains life in every creature that breathes.

We stand on one world and we breathe the one air. That may seem completely obvious, but we’re living in a time when all kinds of forces want to tear us apart – to separate us from each other and to pit us against each other us on the basis of race or class or religion, gender, nationality, or the status of our citizenship. We’re living in a time when all kinds of forces want to make us suspicious or contemptuous or afraid of each other. Some of these forces come from within us, and some from outside us; and it is our great challenge to stand strong and to say No to hatred, and Yes to love and compassion.
So we have gathered in our glorious diversity – people from all walks of life, people of different ages, backgrounds, and experiences – to stand together, shoulder to shoulder. We need each other. We belong to each other. The only way to create a just and sustainable world is to create that world together.
Each of us may bring to the table a particular concern, such as labor or health or poverty or racism or immigration or human rights or the environment, but we know that these supposedly separate issues are in fact deeply connected. We will only find a path forward if we walk that path together – if we reach out to each other, and show up for each other, and work together to heal our shared planet from the threat of climate chaos and social chaos.

I’m glad we’re standing in front of the State House, for we have many legislative battles ahead of us as we fight to keep fossil fuels in the ground. I’m especially glad to be standing with other founding members of the brand-new Massachusetts Interfaith Coalition for Climate Action. We are committed to an energy future based on clean, safe renewable energy such as sun and wind. Just as important, we are committed to a human future based on justice and compassion. In a society that too often treats people like objects, and corporations like people, we intend to lift up the deep wisdom found at the heart of every religion: the Earth and all its residents are sacred.
We call upon the power of love, the sacred power that created all things and that holds all things together. With that love in our hearts, we stand strong on this good earth. We breathe deep of this sweet air. And we commit ourselves to walk this walk together.